It is the largest organ of the body, with a total area of about 20 square feet. The skin protects us from microbes and the elements, helps regulate body temperature, and permits the sensations of touch, heat, and cold.
It has three layers:
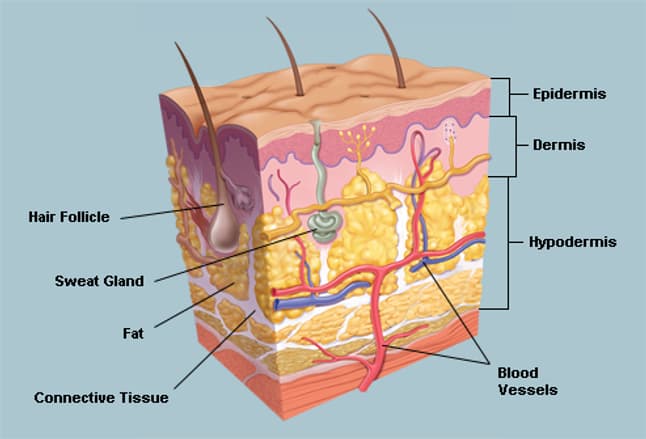
The epidermis
the outermost layer of it, provides a waterproof barrier and creates our tone. It’s main roles are:
- to make new skin cells
- to give the skin its color
- to protect the body from the external environment
Keratinocytes are the most common type of cells within the epidermis. Their job is to act as a barrier against bacteria, parasites, fungi, viruses, heat, ultraviolet (UV) rays, and water loss.
The epidermis contains no blood vessels. The color of the skin comes from a pigment called melanin, which is produced by melanocytes. These are found in the epidermis and protect the skin from UV rays.
The dermis
beneath the epidermis, contains tough connective tissue, hair follicles, and sweat glands. its main roles are:
- to make sweat and oil
- to provide sensation and blood to the skin
- to grow hair
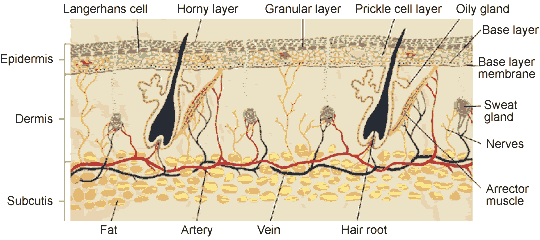
The deeper subcutaneous tissue (hypodermis)
is made of fat and connective tissue.
Functions of it
Some of the many roles of it include:
- Protecting against pathogens. Langerhans cells in it is part of the immune system.
- Storing lipids (fats) and water.
- Creating sensation through nerve endings that detect temperature, pressure, vibration, touch, and injury.
- Controlling water loss by preventing water from escaping by evaporation.
- Providing water resistance by preventing nutrients from being washed from it
- Helping with thermoregulation by producing sweat and dilating blood vessels, which helps keep the body cool. “Goosebumps” and blood vessel constriction help people retain heat.

Aging skin
As a person gets older, their skin changes. It becomes thinner and more easily damaged. The epidermis becomes slower at replacing dead it cells and the process of healing slows. Overall, a person will have less it, and it becomes less elastic.
Older adults may find that their skin becomes more dry, irritated, and thin. It may itch more, bruise, and become infected more easily.
There are a number of reasons why the skin goes through these changes as a person ages. These includeTrusted Source environmental, genetic, and cellular factors. Hormonal changes can also impact it, as well as exposure to UV rays, which increases the risk of skin cancer.
Recommended skin care for older adults places particular emphasis on moisturizing it and keeping it protected from the sun.

Types of skin disease
Acne
It is caused when blocked it follicles from a plug caused by oil from glands, bacteria, and dead cells clump together and swell.
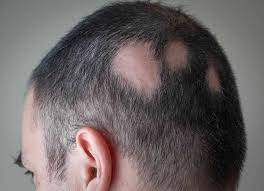
Alopecia Areata
It is a condition that attacks your hair follicles (they make hair). In most cases, hair falls out in small, round patches.
Atopic Dermatitis
It is disease causing much itchiness. Scratching leads to redness, swelling, cracking, weeping clear fluid, crusting, and scaling.
Epidermolysis Bullosa
It is a group of diseases causing painful blisters to form on it. These blisters can cause problems if they become infected.
Ichthyosis
It is a disorder that causes dry, thickened skin that may look similar to fish scales.
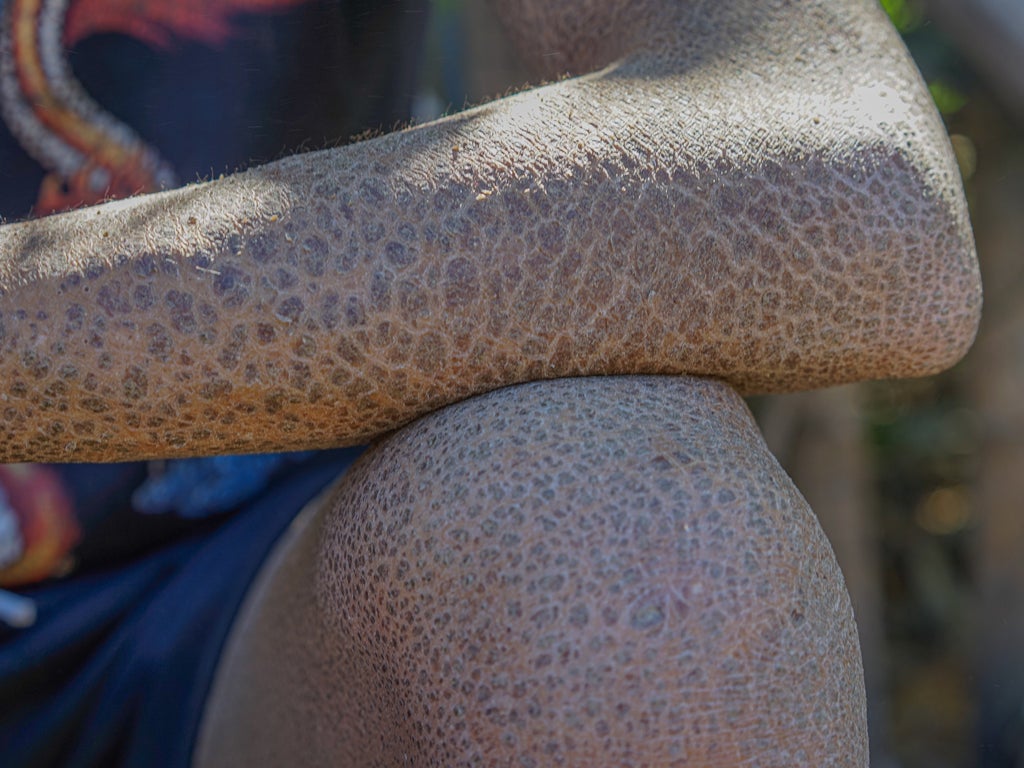
Pachyonychia Congenita
is a rare disorder causing thick nails and painful calluses on the bottoms of the feet and other symptoms.
Pemphigus
It is a disease where the immune system attacks healthy cells in the top layer of it, resulting in blisters.
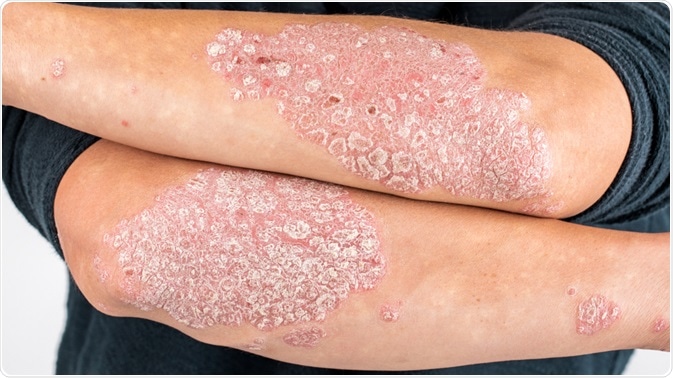
psoriasis
Psoriasis is a skin disease that causes red, scaly that may feel painful, swollen, or hot
Raynaud’s Phenomenon
It is a disease that affects blood vessels. It causes your body to not send enough blood to the hands and feet for a period of time.
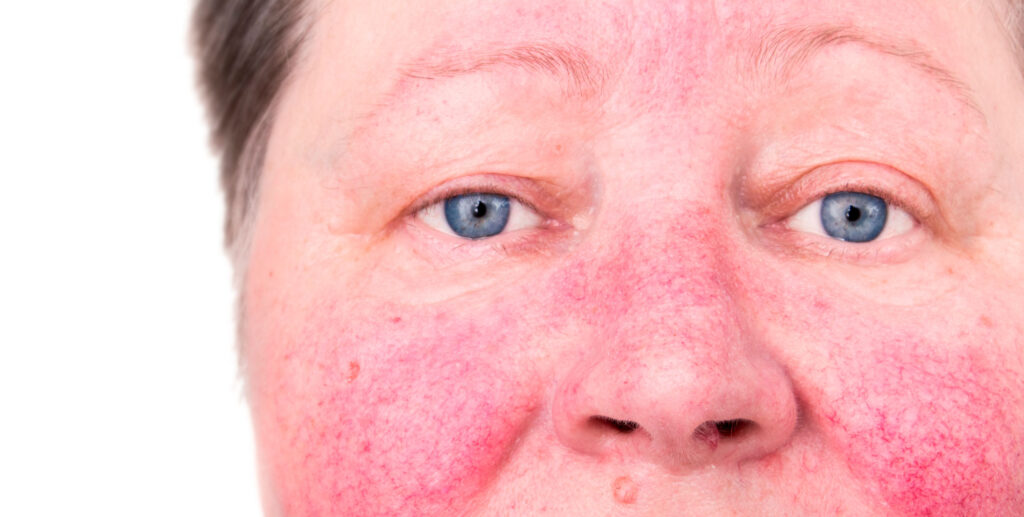
Rosacea
It is a long-term disease that causes reddened skin and pimples, usually on the face. It can also make it thicker and cause eye problems.
Scleroderma
Scleroderma causes patches of tight, hard skin, but can also harm your blood vessels and organs
Vitiligo
Vitiligo is a disorder that causes patches of skin to become white. It happens because cells that make color in your skin are destroyed.
