so who am I?
- My name is Vitamin C or ascorbic acid , a hydrosoluble vitamin derived from glucose metabolism , Humans cannot synthesize ascorbic acid as they lack an enzyme called gulonolactone oxidase.
- Concentrations in plasma and leukocytes reflect the levels of the diet and body deposits respectively of this vitamin.
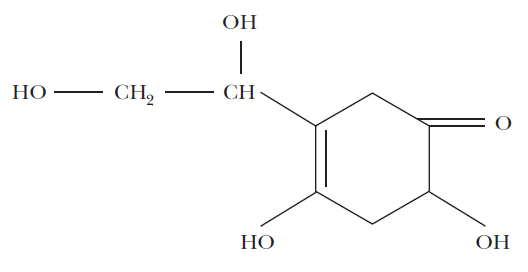
Where do you find me?
Among foods with high vitamin C levels are :
- Tomatoes
- Potatoes
- citric fruits such as limes, oranges and lemons
- peppers (the richest)
- strawberries
- broccoli

How much vitamin C do I need?
| Recommended Dietary Allowances (RDAs) for Vitamin C | ||||
| Age | Male | Female | Pregnancy | Lactation |
| 0–6 months | 40 mg* | 40 mg* | ||
| 7–12 months | 50 mg* | 50 mg* | ||
| 1–3 years | 15 mg | 15 mg | ||
| 4–8 years | 25 mg | 25 mg | ||
| 9–13 years | 45 mg | 45 mg | ||
| 14–18 years | 75 mg | 65 mg | 80 mg | 115 mg |
| 19+ years | 90 mg | 75 mg | 85 mg | 120 mg |
| Smokers | Individuals who smoke require 35 mg/day more vitamin C than nonsmokers. |
You should be able to get all the vitamin C you need from your daily diet.

It vital roles:
- it is required for the biosynthesis of collagen, L-carnitine, and certain neurotransmitters (Collagen is an essential component of connective tissue, which plays a vital role in wound healing)
- It is also involved in protein metabolism
- it is also an important physiological antioxidant and has been shown to regenerate other antioxidants within the body, including alpha-tocopherol (vitamin E) .
- Ongoing research is examining whether it, by limiting the damaging effects of free radicals through its antioxidant activity, might help prevent or delay the development of certain cancers, cardiovascular disease, and other diseases in which oxidative stress plays a causal role.
- In addition to its biosynthetic and antioxidant functions, it plays an important role in immune function and improves the absorption of nonheme iron , the form of iron present in plant-based foods..

Vitamin C Deficiency
- Acute vitamin C deficiency leads to scurvy . The timeline for the development of scurvy varies, depending on vitamin C body stores, but signs can appear within 1 month of little or no vitamin C intake (below 10 mg/day). Initial symptoms can include:
- fatigue (probably the result of impaired carnitine biosynthesis)
- malaise
- inflammation of the gums
As vitamin C deficiency progresses, collagen synthesis becomes impaired and connective tissues become weakened, causing petechiae, ecchymoses, purpura, joint pain, poor wound healing, hyperkeratosis, and corkscrew hairs.
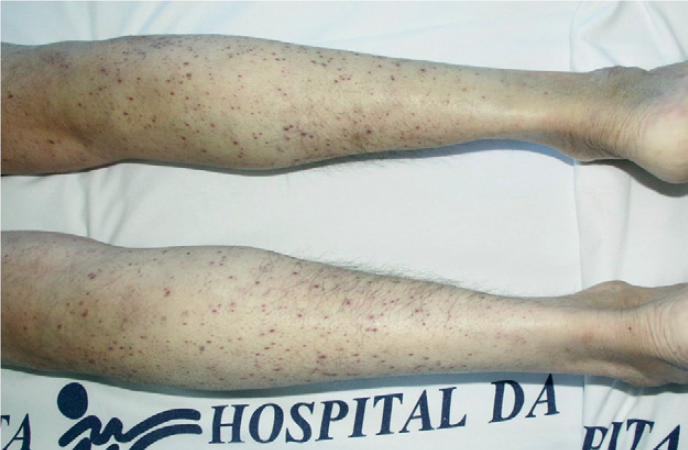
- Additional signs of scurvy include :
- depression
- swollen
- bleeding gums
- loosening or loss of teeth due to tissue and capillary fragility . Iron deficiency anemia can also occur due to increased bleeding and decreased nonheme iron absorption secondary to low it intake . In children, bone disease can be present . Left untreated, scurvy is fatal.
- Until the end of the 18th century, many sailors who ventured on long ocean voyages, with little or no vitamin C intake, contracted or died from scurvy. During the mid-1700s, Sir James Lind, a British Navy surgeon, conducted experiments and determined that eating citrus fruits or juices could cure scurvy, although scientists did not prove that ascorbic acid was the active component until 1932 .
- Today, vitamin C deficiency and scurvy are rare in developed countries . Overt deficiency symptoms occur only if it intake falls below approximately 10 mg/day for many weeks . it deficiency is uncommon in developed countries but can still occur in people with limited food variety.
Health Risks Caused by Excessive Doses of L-Ascorbic Acid
- Vitamin C has low toxicity and is not believed to cause serious adverse effects in case of excessive doses. The most common complaints are:
- Diarrhea
- Nausea
- abdominal cramps
- and other gastrointestinal disturbances due to the osmotic effect of it that is not absorbed in the GI tract.
- Because of its role in enhancing the absorption of non-heme iron, excessive doses of it may increase the absorption of excess iron. This does not cause side effects in healthy people, but is a concern in individuals with hereditary hemochromatosis, as high doses of it can worsen iron overload and cause tissue damage.
- Other reported effects include decreased vitamin B12 and copper levels, accelerated metabolism or excretion of ascorbic acid, and erosion of tooth enamel. Some of these conclusions, however, were the result of an artifact examination, and additional studies have not confirmed these observations.
References:

Very nice